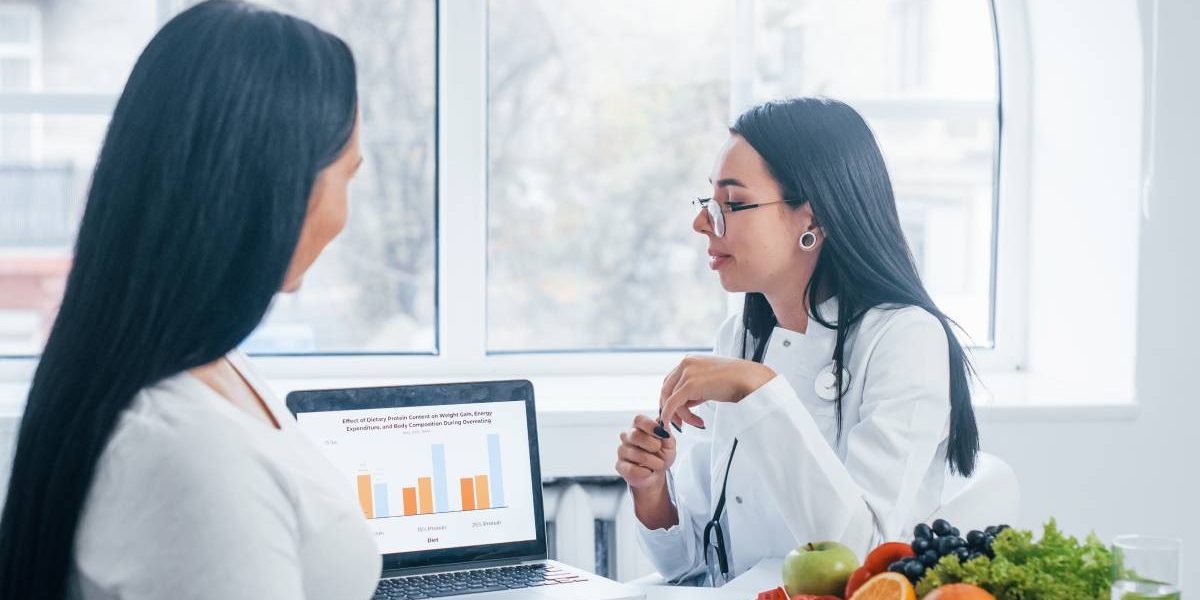
In recent years, the connection between physical and mental health has led to the emergence of metabolic mental health, a field exploring how metabolic processes impact mental well-being.
Traditionally, metabolic health refers to how the body handles energy, including blood sugar regulation, cholesterol, and fat distribution.
Disruptions in these processes, such as insulin resistance and inflammation, can significantly affect mood and cognition.
Mental health issues like anxiety and depression can, in turn, worsen metabolic function. By focusing on improving metabolic health through lifestyle changes, individuals can enhance both their physical and mental health. This article explores how improving metabolic health can lead to better mental health and overall well-being.
What is Metabolic Mental Health?
Metabolic health traditionally refers to how the body processes energy and nutrients, affecting blood sugar, cholesterol, and body fat distribution.
Recently, a field called metabolic mental health has emerged, exploring how metabolic processes influence mental well-being, mood, cognition, and mental health disorders.
Research shows that factors like insulin sensitivity, blood sugar regulation, inflammation, and the gut microbiome can impact brain function.
Conversely, mental health issues like depression and anxiety can affect metabolic processes, creating a feedback loop linking physical and mental health.
How Metabolic Health Influences Mental Health
Metabolic health and mental health are deeply interconnected. When metabolic processes are disrupted, they can negatively impact the brain’s ability to function properly. For example:
- Blood Sugar and Brain Function: High blood sugar, insulin resistance, and fluctuations in glucose levels are closely linked to mood changes, cognitive decline, and disorders such as depression and anxiety. The brain relies on glucose for energy, and when blood sugar levels are unstable, it can lead to fatigue, irritability, and difficulties concentrating. Chronic high blood sugar can impair brain function over time, increasing the risk of developing mental health issues.
- Inflammation and Mental Health: Chronic inflammation is common in metabolic disorders and contributes to mental health issues. It can affect brain neurotransmitter systems, leading to symptoms like low mood, cognitive dysfunction, and depression. Conditions such as obesity and metabolic syndrome, marked by high inflammation, can worsen mental health problems.
- The Gut-Brain Connection: The gut microbiome, consisting of trillions of bacteria, significantly impacts mental health. It is closely linked to metabolic health, influencing nutrient absorption, hormone regulation, and immune function. Imbalances in the gut microbiome are associated with mood disorders like anxiety and depression, while a healthy gut supports both metabolic function and mental well-being.
- Hormonal Imbalance and Mental Health: Metabolic health is strongly linked to hormone regulation, particularly hormones like cortisol, thyroid hormones, and sex hormones. Imbalances in these hormones can lead to mental health problems. For instance, high cortisol levels due to chronic stress or metabolic dysfunction can contribute to anxiety and depression, while thyroid imbalances can cause fatigue, brain fog, and mood disturbances.
How Can You Improve Your Metabolic Health?
Improving your metabolic health is a multifaceted process that involves adopting lifestyle changes, making dietary improvements, and engaging in physical activity. Here are some steps you can take to support your metabolic and mental health:
Balanced Diet
Eating a nutrient-rich, balanced diet is one of the most important factors in improving metabolic health. A diet high in whole foods, including vegetables, fruits, lean proteins, whole grains, and healthy fats, supports metabolic processes and helps maintain healthy blood sugar levels.
Foods rich in omega-3 fatty acids, such as fish, walnuts, and flaxseeds, are particularly beneficial for both metabolic health and brain function. Additionally, avoiding highly processed foods, sugary snacks, and refined carbohydrates can help regulate blood sugar and reduce inflammation.
Regular Exercise
Physical activity is vital for metabolic health, improving insulin sensitivity, blood sugar regulation, and reducing inflammation.
Aerobic exercises like walking, cycling, or swimming promote cardiovascular health, while strength training builds muscle mass, boosting metabolism and blood sugar regulation. Exercise also releases endorphins, enhancing mood and alleviating anxiety and depression.
Adding intermittent fasting, like the 16/8 method to regular exercise can further optimize metabolic health. This method, which involves fasting for 16 hours and eating within an 8-hour window, enhances insulin sensitivity, regulates blood sugar, and reduces body fat, improving overall well-being.
Stress Management
Chronic stress can negatively affect both metabolic health and mental well-being. When the body is under stress, it produces cortisol, a hormone that, in high amounts, can contribute to weight gain, inflammation, and metabolic dysfunction.
Stress management techniques such as meditation, mindfulness, yoga, and deep breathing exercises can help lower cortisol levels and improve both physical and mental health.
Sleep Quality
Poor sleep is a major factor that disrupts metabolic processes and can worsen mental health conditions. Sleep deprivation impairs insulin sensitivity, increases appetite, and leads to weight gain, all of which negatively affect metabolism.
Additionally, inadequate sleep can contribute to mood disorders like depression and anxiety. Prioritizing good sleep hygiene, such as setting a consistent sleep schedule, avoiding caffeine late in the day, and creating a relaxing bedtime routine, can help improve both metabolic health and mental well-being.
Social Connections
Social support is essential for mental health, and strong social connections can positively affect metabolic health.
Engaging in social activities, maintaining relationships, and seeking emotional support during difficult times can help reduce stress, promote happiness, and improve cognitive function.
Isolation and loneliness can negatively impact both mental health and metabolic health, so it’s important to stay connected to friends, family, and community.
Supplements
Some supplements, like omega-3 fatty acids, vitamin D, magnesium, and probiotics, may also help improve metabolic health and mental well-being.
Omega-3s, for example, support brain function and reduce inflammation, while magnesium can help regulate blood sugar levels and improve sleep quality.
However, supplements should be used in conjunction with a healthy diet and lifestyle, and it’s always a good idea to consult with a healthcare provider before adding new supplements to your routine.
Am I Metabolically Unhealthy?
Metabolic health can be assessed through several indicators, including blood sugar levels, cholesterol levels, body fat percentage, and blood pressure. If you are experiencing any of the following symptoms or conditions, it may indicate that you are metabolically unhealthy:
- Chronic Fatigue: Feeling excessively tired or fatigued despite adequate rest could indicate an imbalance in metabolic processes, such as insulin resistance or poor blood sugar regulation.
- Weight Gain: Unexplained weight gain, especially around the abdominal area, is a common sign of metabolic dysfunction and can be a result of poor insulin sensitivity or high cortisol levels.
- Mood Swings and Irritability: Fluctuations in blood sugar and hormonal imbalances can contribute to mood swings, irritability, anxiety, and depression.
- Increased Hunger or Cravings: Constant feelings of hunger or cravings for sugary or high-carbohydrate foods can indicate poor blood sugar regulation and insulin resistance.
- Elevated Blood Pressure or Cholesterol: High blood pressure and elevated cholesterol levels are key indicators of metabolic dysfunction and can increase the risk of heart disease and stroke.
- Difficulty Concentrating or Brain Fog: Metabolic health impacts brain function, and poor blood sugar regulation or inflammation can contribute to cognitive issues like brain fog, memory problems, and difficulty concentrating.
If you are concerned about your metabolic health, it’s important to consult with a healthcare provider. A medical professional can assess your metabolic health through blood tests and provide personalized recommendations for improving your overall well-being.
Conclusion
Metabolic mental health is an emerging field that recognizes the close relationship between metabolic health and mental well-being.
By focusing on factors such as blood sugar regulation, inflammation, gut health, and stress management, individuals can improve both their physical health and mental health.
Adopting healthy lifestyle habits such as eating a balanced diet, exercising regularly, managing stress, and prioritizing sleep can help support metabolic and mental health.
If you are concerned about your metabolic health, seeking medical advice and making positive changes to your lifestyle can help you achieve better overall well-being.